The COVID-19 pandemic caused long-term disruptions in the labor markets globally during 2020. At the onset of the coronavirus outburst, consumer spending began to decline notably in retail as well as in recreational sectors. In addition, unemployment also witnessed an upsurge in the countries on account of being affected by the global crisis.
“According to a report by the International Labor Organization (ILO), approximately 114 million people in the world lost their jobs pertaining to the imposed lockdown in 2020, which further resulted in a labor income loss of USD 3.7 million or 4.4 percent of the global GDP of 2019.”
On the contrary, the public health crisis also led to the emergence of several new job positions. The people who were fortunate to keep their jobs, on the other hand, found solace in working from homes as the offices closed down.
Which Industries have been Hit the Hardest by the Pandemic?
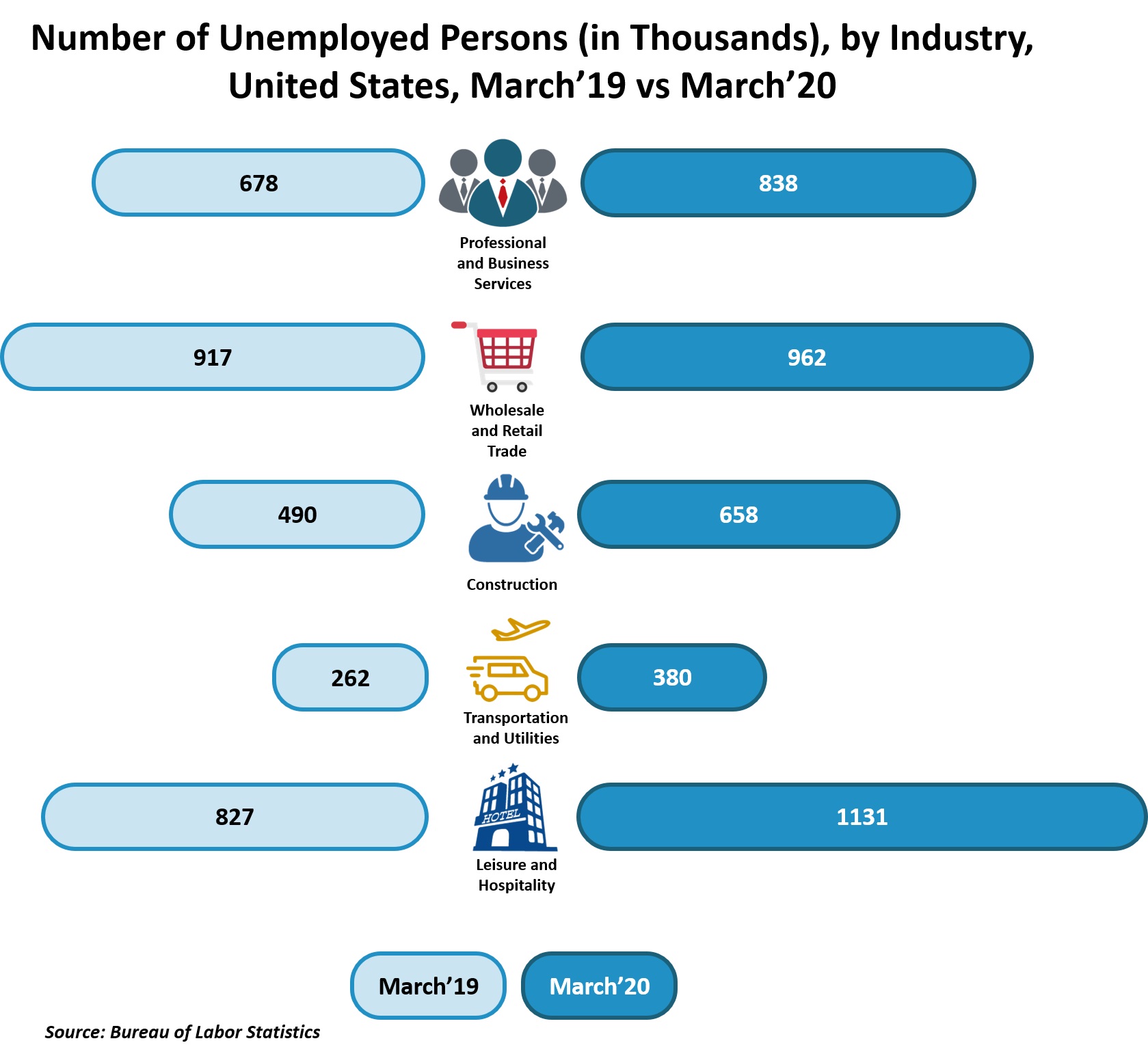
- Leisure and Hospitality
With restaurants, bars, and public halls, being shut down permanently or operating in a limited capacity, many people succumbed to job losses. In addition, both local and international visitor expenditure observed a downfall prior to the pandemic. As per the World Travel and Tourism Council, the total money spent by a domestic visitor decreased by 45 percent, while that by an international visitor declined by an unprecedented 69.4 percent. Furthermore, food services and drinking places, in particular, had the highest occupational damage during the COVID-19 outburst.
- Travel and Transportation
The world witnessed a torrent of layoffs in the airline and railroad businesses. As more and more people felt uncomfortable traveling, ground and air passenger transportation industries ushered in a slew of job losses. In 2020, the travel and tourism sector witnessed a loss of more than 100 million jobs across the globe. Asia Pacific region was hit the hardest, accounting for an unemployment value of about 63 million jobs in the same year. The pandemic also resulted in job losses among truck drivers owing to the temporary shutdown of businesses, which in turn steered the course for a decrease in the need for supplies.
- Construction
In one of ILO’s reports depicting world employment and social outlook trends in 2020, it was stated that the global employment in the construction industry declined by a whopping 8.4 percent in the second quarter of the year, and by 2.2 percent in the third quarter of the same year. The community of specialty trade contractors in the construction sector witnessed the largest proportion of job losses in the wake of the pandemic. Additionally, there was a slowdown in renovations at workplaces and office buildings owing to the imposition of worldwide lockdown. This factor posed a negative impact on infrastructure-based jobs globally. However, the industry recovered some of the lost jobs at the beginning of 2021.
- Retail Trade
The retail trade businesses witnessed a notable shed of jobs in 2020. According to the World Trade Organization, world merchandise trade volume fell by 5.3 percent in 2020, which is estimated to increase by 8 percent by the end of 2021. On the contrary, the trade growth is expected to decline again in 2022 by 4 percent. As most of the occupations in the industry require people to work side by side, practicing social distancing in the work facility posed itself as a huge challenge. Amongst all, the largest job losses occurred in clothing and clothing accessories, furniture, and sporting goods stores.
- Professional & Business Services
The professional & business services sector includes the job profiles of accountants, lawyers, engineers, and temporary workers. The World Economic Forum conducted a survey of the future of jobs in 2020, which depicted that 11.6 percent of workers in the professional services industry were at risk of displacement that year. Along with this, accounting, bookkeeping, and payroll clerks made the list of the top ten most redundant job roles in this sector. Also, temporary help workers, who worked on a per-project basis, compromised for a considerable portion of the total industry losses. However, employment in the sector observed a rise in November 2020 but dipped again in February 2021.
Which Industries Gained the Most from the Pandemic?
- E-Learning
The COVID-19 pandemic resulted in the shutdown of schools all across the world. According to UNESCO, as of mid-April 2020, approximately 1.3 billion children in 186 countries were affected by school closure. One year into the global COVID-19 pandemic, over 100 million children are predicted to fall below the minimum proficiency level in reading as a result of the health crisis. To combat these issues, a large number of schools and colleges across the world are shifting to distance learning. Many teachers, especially the ones who have always followed conventional schooling methods, were seen trying web apps such as Google Classroom and Zoom for teaching. Furthermore, massive open online courses (MOOCs) and webinars witnessed renewed interest among adults and business owners in recent times.
- Software and Remote Working Tools
With the deployment of full or partial lockdowns, many businesses turned to remote working apps and software to maintain appropriate levels of productivity. Many tech companies’ shares fell in value, whereas the companies developing enterprise video conferencing proprietary programs gained millions of new customers. The sector is also estimated to benefit significantly in the near future as organizations began to view remote working tools as a means to gravitate towards the trend of working from home. For instance, Zoom Video Communications Inc. reported total revenue of more than USD 663 million in the second quarter of the fiscal year 2021. In addition, the total cash, cash equivalents, and marketable securities of the firm as of July 31, 2020, were almost USD 1.5 billion.
- Entertainment
The home entertainment sector observed a surge in online streaming owing to travel bans, social distancing measures, and mandated self-quarantines for returning travelers. The increasing number of new video entrants helped push digital viewership to the highest levels in 2020. In the second quarter (Q2) of 2020, Netflix recorded an addition of approximately 11 million paid memberships, up from 2.7 million in the previous year’s Q2. The total number of global paid memberships of this OTT platform was calculated at about 193 million in the same quarter. Along with this, social media influencers and immersive games also gained new users as people were looking for ways to interact with the outside world.
- Healthcare
The coronavirus crisis has led to an increase in demand for medical supplies and care. In 2021, Johnson & Johnson, one of the largest medical equipment companies, alone observed sales of approximately USD 82 billion. Moreover, huge investments are continuously being poured in for manufacturing vaccines for COVID-19, which in turn, is expected to largely boost the growth of this industry in the near future. Apart from this, the increasing geriatric population globally is also projected to augment the demand for medical supplies in the upcoming years as growing age is a major risk factor for many diseases. As per the WHO, the proportion of the world's population over 60 years will nearly double from 12% to 22%, between 2015 and 2050. On the other hand, by 2030, 1 in every 6 persons will be aged 60 years or above.
- Electronic Transfers
With the inception of the pandemic, people have become more conscious about their hygiene. As notes and coins can be carriers for different types of germs, including the coronavirus that causes COVID-19, many different ways of online money transfer are being adopted around the world. It is estimated that about 1 billion people globally used a mobile payment app in 2020. Moreover, this user base is expected to reach more than 1.2 billion by the first half of 2030.
How Will the Landscape of Jobs Change in the Future?
- Higher Adoption of Automated Technologies Amongst Businesses
As of July 2020, around two-thirds of businesses globally were reported to increase their investments in automation and artificial intelligence. China was one of the major countries to allocate a high budget for the development of the robotics sector. Moreover, many industries, including healthcare, consumer goods delivery, and restaurants, witnessed an increased deployment of automation on a global level. For instance, Flippy, a cooking robot developed by Miso Robotics, is widely being used in restaurants all across the US. The robot is able to flip over 10,000 burgers and fries in more than 12,000 baskets every month. Apart from this, a robot named Pepper was deployed in multiple malls in Germany for reminding shoppers to wear masks, thus, helping in the battle against COVID-19.
- Increase in Remote Working
It is calculated that as of April 2021, more than 47% of the employees are likely to work remotely post COVID-19 outbreak, compared to about 30 percent before the pandemic. Moreover, several organizations are emphasizing highly on remote work operations that allow employees to adjust their working strategies, promote digital collaboration and enable the formation of a team that is willing to adapt to an uncertain future.
How can Research Nester Help You?
With the drastic impact of the coronavirus outbreak on the global economy, organizations all around the world are in immediate need to revive their businesses at the earliest. At Research Nester, our sole aim is to offer unprecedented services to help our clientele attain maximum profits. Our services include strategic market research and consulting with an unbiased and unparalleled approach towards helping global industrial players, conglomerates, and executives to make wise decisions for their future investments.







































































